Why Self-Acceptance Can Be the Key to Avoiding Burnout
In today’s fast-paced society, it’s easy to push ourselves past our limits without realizing the toll it takes. Long working hours, constant digital distractions, and the pressure to achieve more often lead to stress and fatigue. Yet our bodies are constantly giving us signals—small warnings that something isn’t right. Too often, we ignore them until exhaustion sets in. By tuning into these signals, we can prevent burnout before it takes over. Interestingly, developing awareness of physical and emotional cues goes hand in hand with learning to accept our imperfections. That’s why this thoughtful piece on self-acceptance can complement the idea of listening to your body, helping you build resilience and restore balance in daily life.
It Helps You See Early Signs of Burnout
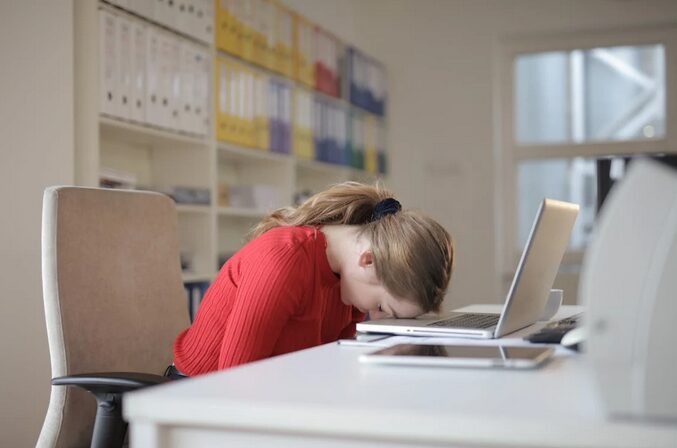

One of the most powerful ways to avoid burnout is by paying attention to fatigue. Fatigue isn’t just about being tired after a long day; it’s about that persistent sense of heaviness that doesn’t go away even with rest. Your body might show you clues—such as difficulty concentrating, slower reaction times, or constant yawning. By acknowledging these signs early, you can step back before exhaustion deepens. Taking short breaks, adjusting your workload, or even giving yourself permission to rest for a day can prevent prolonged stress. Recognizing these signals is a form of self-respect, and it allows you to protect your energy instead of depleting it.
It Gives You Better Sleep and Rest
Sleep is one of the clearest indicators of overall well-being, and yet it’s often the first thing people sacrifice when deadlines or responsibilities pile up. Trouble falling asleep, restless nights, or waking up feeling drained are signals that your body is struggling. Lack of sleep doesn’t just impact energy—it clouds decision-making, weakens emotional resilience, and reduces productivity. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene, like maintaining a consistent bedtime or lessening screen time before bed, can restore balance. By honoring the body’s need for rest, you can build a stronger foundation for both physical and mental health, making burnout less likely to take root.
It Ensures Emotional Awareness and Mental Check-ins
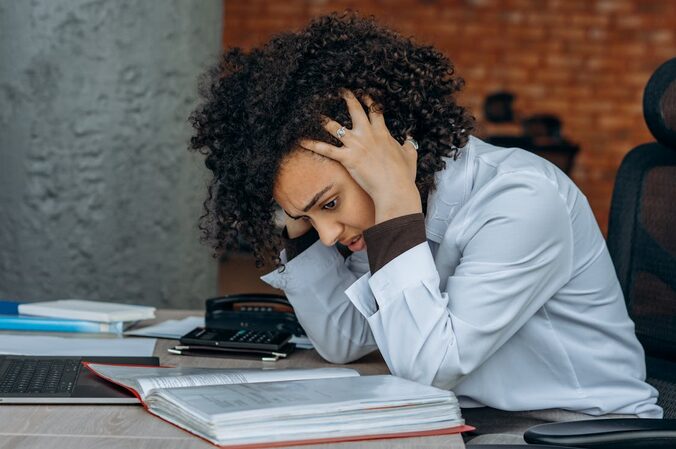

Accepting yourself isn’t only about physical sensations—it also involves being honest about emotions. Irritability, anxiety, or a constant sense of overwhelm are as important as physical fatigue. These emotional signals are often early indicators that you’re under too much pressure. Taking time each day for mental check-ins—whether through journaling, meditation, or a mindful walk—helps bring these emotions to the surface. Once you notice them, you can take steps to address the root causes rather than ignoring them until burnout sets in. Giving yourself space to process emotions makes it easier to regain perspective and restore energy.
Burnout doesn’t arrive suddenly—it builds slowly through ignored signals and repeated overexertion. By recognizing fatigue, respecting the physical reactions of stress, valuing proper sleep, and staying aware of emotional states, you can prevent it from taking control of your life. Listening to your body is an act of self-care that strengthens your ability to thrive in demanding environments. Small daily adjustments can protect both your health and productivity, ensuring you continue to perform well without sacrificing your well-being.…

















 As with any medical solution, there are potential risks associated with
As with any medical solution, there are potential risks associated with 
 One way to improve the quality of care in health facilities is to encourage patients to speak up if they don’t feel comfortable. This can be done by creating an open and welcoming environment where patients feel their concerns will be heard and addressed. Additionally, staff need training on listening and responding to patient concerns. By creating a space where patients feel comfortable speaking up, we can ensure that they receive the best possible care.
One way to improve the quality of care in health facilities is to encourage patients to speak up if they don’t feel comfortable. This can be done by creating an open and welcoming environment where patients feel their concerns will be heard and addressed. Additionally, staff need training on listening and responding to patient concerns. By creating a space where patients feel comfortable speaking up, we can ensure that they receive the best possible care. All staff members in health facilities should know basic first aid and CPR. This training can help staff members feel more confident in their ability to provide care, and it can also help them respond quickly and effectively in an emergency. Additionally, this training can help create a safe culture in the facility. We can create a safer environment by ensuring that we train all staff members in basic first aid and CPR.
All staff members in health facilities should know basic first aid and CPR. This training can help staff members feel more confident in their ability to provide care, and it can also help them respond quickly and effectively in an emergency. Additionally, this training can help create a safe culture in the facility. We can create a safer environment by ensuring that we train all staff members in basic first aid and CPR. Another way to improve the quality of care in health facilities is to create a policy for handling complaints from patients or families. This policy should outline the steps they will take to address the complaint and the process for investigating and resolving the issue. Additionally, this policy should ensure that the facility takes complaints seriously and that patients or families feel their concerns are addressed. For example, the policy might state that the facility investigates complaints within 24 hours, giving a response 48 hours.…
Another way to improve the quality of care in health facilities is to create a policy for handling complaints from patients or families. This policy should outline the steps they will take to address the complaint and the process for investigating and resolving the issue. Additionally, this policy should ensure that the facility takes complaints seriously and that patients or families feel their concerns are addressed. For example, the policy might state that the facility investigates complaints within 24 hours, giving a response 48 hours.…
 Eggs are known to increase testosterone levels. They are also known to help build muscle because they are rich in protein. Many people do not know that eggs have many vitamins. Choline, which is also found in eggs, is another important mineral that most people lack.
Eggs are known to increase testosterone levels. They are also known to help build muscle because they are rich in protein. Many people do not know that eggs have many vitamins. Choline, which is also found in eggs, is another important mineral that most people lack. Pomegranate has been shown to increase testosterone levels in men by up to 24%. It also contains antioxidants and nutrients such as folic acid, potassium, fiber, and several vitamins, which can help improve overall health. It can reduce the risk of prostate cancer in men.
Pomegranate has been shown to increase testosterone levels in men by up to 24%. It also contains antioxidants and nutrients such as folic acid, potassium, fiber, and several vitamins, which can help improve overall health. It can reduce the risk of prostate cancer in men.
 Innovative technologies have applied their potential to product design and development over the past few decades, achieving amazing results. According to the study shown in
Innovative technologies have applied their potential to product design and development over the past few decades, achieving amazing results. According to the study shown in  Incorporating AI can allow medical to automate the analysis of these things and be efficient in other aspects of the healthcare industry. Besides, AI successfully implements a significant number of user sessions to find bugs that exist. Merchandise is always developed with customers in mind, and only if the merchandise resonates with customers can it be successful. It needs to be easy to use and enjoyable. Therefore, when looking for creative alternatives, designers are expected to think about usage, validate their ideas, analyze possibilities, and develop designs with medical goals in mind.
Incorporating AI can allow medical to automate the analysis of these things and be efficient in other aspects of the healthcare industry. Besides, AI successfully implements a significant number of user sessions to find bugs that exist. Merchandise is always developed with customers in mind, and only if the merchandise resonates with customers can it be successful. It needs to be easy to use and enjoyable. Therefore, when looking for creative alternatives, designers are expected to think about usage, validate their ideas, analyze possibilities, and develop designs with medical goals in mind.
 This change in diet is usually accompanied by various symptoms such as irritability, headaches, difficulty concentrating, nausea, bad breath, stomach pain, sleep disturbances, constipation, confusion and others. For this reason, these signs are also known as keto-flu. Usually, the signs of keto-flu appear within a week and the body begins to lose weight. The weight loss can often be very visible and noticeable.
This change in diet is usually accompanied by various symptoms such as irritability, headaches, difficulty concentrating, nausea, bad breath, stomach pain, sleep disturbances, constipation, confusion and others. For this reason, these signs are also known as keto-flu. Usually, the signs of keto-flu appear within a week and the body begins to lose weight. The weight loss can often be very visible and noticeable.
 Doctors strongly recommend no less than 30 minutes of exercise a day to maintain optimal health. In these cases, biking, jogging, or walking throughout the day to wash your mind and restore your body can do fantastic things for your well-being. You can also buy equipment for your property, standing weights, a rowing machine to go to the gym, or maybe even a yoga mat. Then go to YouTube and find one of the many excellent exercise tools that are available.
Doctors strongly recommend no less than 30 minutes of exercise a day to maintain optimal health. In these cases, biking, jogging, or walking throughout the day to wash your mind and restore your body can do fantastic things for your well-being. You can also buy equipment for your property, standing weights, a rowing machine to go to the gym, or maybe even a yoga mat. Then go to YouTube and find one of the many excellent exercise tools that are available. By closing one eye for 20 minutes, you can give your body and mind a break after exerting yourself to the max for a long time, as well as recharge your energy for the rest of the day. Researchers have studied the effects of regular naps and found positive consequences for people in various work environments, improving work efficiency, problem-solving skills, and creativity.
By closing one eye for 20 minutes, you can give your body and mind a break after exerting yourself to the max for a long time, as well as recharge your energy for the rest of the day. Researchers have studied the effects of regular naps and found positive consequences for people in various work environments, improving work efficiency, problem-solving skills, and creativity. Constantly try to eat whole foods instead of benefiting from them. Habitual consumption of junk food may be tasty, but it has long-term effects. If you don’t have to give up flavor, consider grilling your favorite foods for a more earthy taste. You will find a vast selection of recipes available for free on the internet.…
Constantly try to eat whole foods instead of benefiting from them. Habitual consumption of junk food may be tasty, but it has long-term effects. If you don’t have to give up flavor, consider grilling your favorite foods for a more earthy taste. You will find a vast selection of recipes available for free on the internet.…

 Judges choose as to if the individual is eligible for payment and just how much. Throughout this time, the attorneys for each side prepare legal documents. Depositions are also frequently taken during the sessions. All these are interviews that permit the lawyers to ask questions. It’s not strange for a settlement to happen in the courthouse during the jury selection procedure.
Judges choose as to if the individual is eligible for payment and just how much. Throughout this time, the attorneys for each side prepare legal documents. Depositions are also frequently taken during the sessions. All these are interviews that permit the lawyers to ask questions. It’s not strange for a settlement to happen in the courthouse during the jury selection procedure.
 Can you realize there is insufficient time for all? If that is the case, it’s most likely because you aren’t scheduling your own time efficiently. This occurs when you run continuously, moving from 1 thing into another, without considering what as a whole. Establish specific due dates and deadlines to get everything that will help you keep on track and have additional time for yourself and your loved ones. No matter what, planners enable you to remain on track with every individual task you will need to finish and motivate you to proceed to another effectively and economically.
Can you realize there is insufficient time for all? If that is the case, it’s most likely because you aren’t scheduling your own time efficiently. This occurs when you run continuously, moving from 1 thing into another, without considering what as a whole. Establish specific due dates and deadlines to get everything that will help you keep on track and have additional time for yourself and your loved ones. No matter what, planners enable you to remain on track with every individual task you will need to finish and motivate you to proceed to another effectively and economically. As you may imagine, planners assist you to keep healthy in a vast assortment of means. It helps your bodily health by allowing you to track things such as exercise and diet. You can schedule regular physician and dentist appointments, and be sure you’re getting sufficient fresh oxygen and vitamin D by merely scheduling times spent outdoors. You get emotional health benefits by lowering tension and anxiety and having journaling webpages for when you only need a great brain dump. This is very important to your own personal and professional life. Even though many men and women consider productivity as it pertains to their job, you want to be productive in your home.
As you may imagine, planners assist you to keep healthy in a vast assortment of means. It helps your bodily health by allowing you to track things such as exercise and diet. You can schedule regular physician and dentist appointments, and be sure you’re getting sufficient fresh oxygen and vitamin D by merely scheduling times spent outdoors. You get emotional health benefits by lowering tension and anxiety and having journaling webpages for when you only need a great brain dump. This is very important to your own personal and professional life. Even though many men and women consider productivity as it pertains to their job, you want to be productive in your home.
 Telehealth is the phase in which information technology is transitioning into healthcare. This phase is underway to enable healthcare providers to deliver telehealth services efficiently and seamlessly. It depends on the type of ceremony you want and the software you use.
Telehealth is the phase in which information technology is transitioning into healthcare. This phase is underway to enable healthcare providers to deliver telehealth services efficiently and seamlessly. It depends on the type of ceremony you want and the software you use.
 One of the most important things you can do with telemedicine is to make an appointment for an in-person visit. Depending on your
One of the most important things you can do with telemedicine is to make an appointment for an in-person visit. Depending on your 
 Korean red ginseng has been used to stimulate male sexual function, but many studies have tried to confirm its benefits. In a 2002 study involving 45 men with significant erectile dysfunction, the herb helped relieve symptoms of erectile dysfunction and led to “improved stiffness of penile function.” Experts aren’t sure how red ginseng might work, although it is believed to promote nitric oxide synthesis.
Korean red ginseng has been used to stimulate male sexual function, but many studies have tried to confirm its benefits. In a 2002 study involving 45 men with significant erectile dysfunction, the herb helped relieve symptoms of erectile dysfunction and led to “improved stiffness of penile function.” Experts aren’t sure how red ginseng might work, although it is believed to promote nitric oxide synthesis. Drinking antioxidant-rich pomegranate juice has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk for heart disease and high blood pressure. Can pomegranate juice also protect against erectile dysfunction? There’s no evidence of this, but the results of a study published in 2007 were promising. The authors of this study called for more research and said more extensive studies could show pomegranate juice’s power against erectile dysfunction.
Drinking antioxidant-rich pomegranate juice has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk for heart disease and high blood pressure. Can pomegranate juice also protect against erectile dysfunction? There’s no evidence of this, but the results of a study published in 2007 were promising. The authors of this study called for more research and said more extensive studies could show pomegranate juice’s power against erectile dysfunction.

 Before we understand all the advantages of the perfect CBD treatments for dogs, we should know what CBD is. Many cannabinoids can be obtained from the cannabis plant, and this is just one of them. Cannabidiol is not pet safe; it is not psychoactive, so how can CBD help? Dogs have an identical distinct endocannabinoid arrangement that can cooperate with the endocannabinoids released by the brain. But to supplement this endocannabinoid cause of the mind, someone could bestow it. This is precisely why it is also beneficial in dogs, and you can apply CBD oil without any side consequences.
Before we understand all the advantages of the perfect CBD treatments for dogs, we should know what CBD is. Many cannabinoids can be obtained from the cannabis plant, and this is just one of them. Cannabidiol is not pet safe; it is not psychoactive, so how can CBD help? Dogs have an identical distinct endocannabinoid arrangement that can cooperate with the endocannabinoids released by the brain. But to supplement this endocannabinoid cause of the mind, someone could bestow it. This is precisely why it is also beneficial in dogs, and you can apply CBD oil without any side consequences. There are many benefits to using CBD for canine pets. Let’s list some of the most influential; increasing anandamide levels in the blood helps reduce pain sensations. CBD influences nitric oxide, which assists improve the quantity of serotonin that hinders any anxiety and nervousness in multiple organisms and, in this case, in dogs. Since it is widespread to have nausea while undergoing unique treatments such as chemotherapy, CBD helps in this situation and suppresses appetite loss. Overall, it could be said that CBD is a marvel drug for pets in the area. They show superior effectiveness in dogs to cure their problems with many medications and hours of using a veterinarian. Don’t think twice before picking the perfect CBD dog treats to aid them with their wellness troubles.
There are many benefits to using CBD for canine pets. Let’s list some of the most influential; increasing anandamide levels in the blood helps reduce pain sensations. CBD influences nitric oxide, which assists improve the quantity of serotonin that hinders any anxiety and nervousness in multiple organisms and, in this case, in dogs. Since it is widespread to have nausea while undergoing unique treatments such as chemotherapy, CBD helps in this situation and suppresses appetite loss. Overall, it could be said that CBD is a marvel drug for pets in the area. They show superior effectiveness in dogs to cure their problems with many medications and hours of using a veterinarian. Don’t think twice before picking the perfect CBD dog treats to aid them with their wellness troubles.
 However, there is a secret you may not realize. When you want to lose weight permanently and reach your goals, the first thing to do is that you need to embrace the person you are now. Accepting yourself cannot be done if you have not realized that forcing yourself to live in a non-stop battle with your fat and calories cannot get you anywhere. In fact, self-acceptance works in reverse. If you are doubtful, read the following tips and implement them to have better respect and healthy positive body.
However, there is a secret you may not realize. When you want to lose weight permanently and reach your goals, the first thing to do is that you need to embrace the person you are now. Accepting yourself cannot be done if you have not realized that forcing yourself to live in a non-stop battle with your fat and calories cannot get you anywhere. In fact, self-acceptance works in reverse. If you are doubtful, read the following tips and implement them to have better respect and healthy positive body. Ensure you have left out any circumstances that make you feel bad about yourself. Choose a circle that can appreciate and accept who you are, even though you do not talk about your diet, food, or weight. Also, wear clothes that you like and that fit you right now. Eliminate anything that does not fit you from your closet. Being unhappy often leads to food. If you keep opening your refrigerator, you might not be aware that it worsens your body. More importantly, you also have to be aware that your clothes’ sizes vary based on the manufacturer. In this case, keep your body positivity on by not letting their size tell you how you might feel about yourself.
Ensure you have left out any circumstances that make you feel bad about yourself. Choose a circle that can appreciate and accept who you are, even though you do not talk about your diet, food, or weight. Also, wear clothes that you like and that fit you right now. Eliminate anything that does not fit you from your closet. Being unhappy often leads to food. If you keep opening your refrigerator, you might not be aware that it worsens your body. More importantly, you also have to be aware that your clothes’ sizes vary based on the manufacturer. In this case, keep your body positivity on by not letting their size tell you how you might feel about yourself.





 CBD can offer a study that shows that the use of CBD oil directly on the problem area helps reduce inflammation and pain. CBD impacts cannabinoid receptors in the human body and then reduces the inflammation and interact with neurotransmitters. Researchers have found that CBD, unlike some pain relievers, is not addictive and has no adverse effects, but provides powerful relief for chronic pain sufferers. An oral spray called Sativex, a combination of CBD and THC, has been accepted in several European countries and Canada (but not the USA) to treat pain and muscle pain associated with multiple sclerosis.
CBD can offer a study that shows that the use of CBD oil directly on the problem area helps reduce inflammation and pain. CBD impacts cannabinoid receptors in the human body and then reduces the inflammation and interact with neurotransmitters. Researchers have found that CBD, unlike some pain relievers, is not addictive and has no adverse effects, but provides powerful relief for chronic pain sufferers. An oral spray called Sativex, a combination of CBD and THC, has been accepted in several European countries and Canada (but not the USA) to treat pain and muscle pain associated with multiple sclerosis.